
Further, practical treatment approaches (choice and dosing), include discussion of combination/augmentation, treatment failure (adherence/expectations), and relapse prevention are mentioned. Treatment involves a disimpaction (cleanout) phase and a maintenance phase. It happens when a child withholds stool, usually because they are afraid of the pain linked to passing hard stools or have a fear of the toilet.
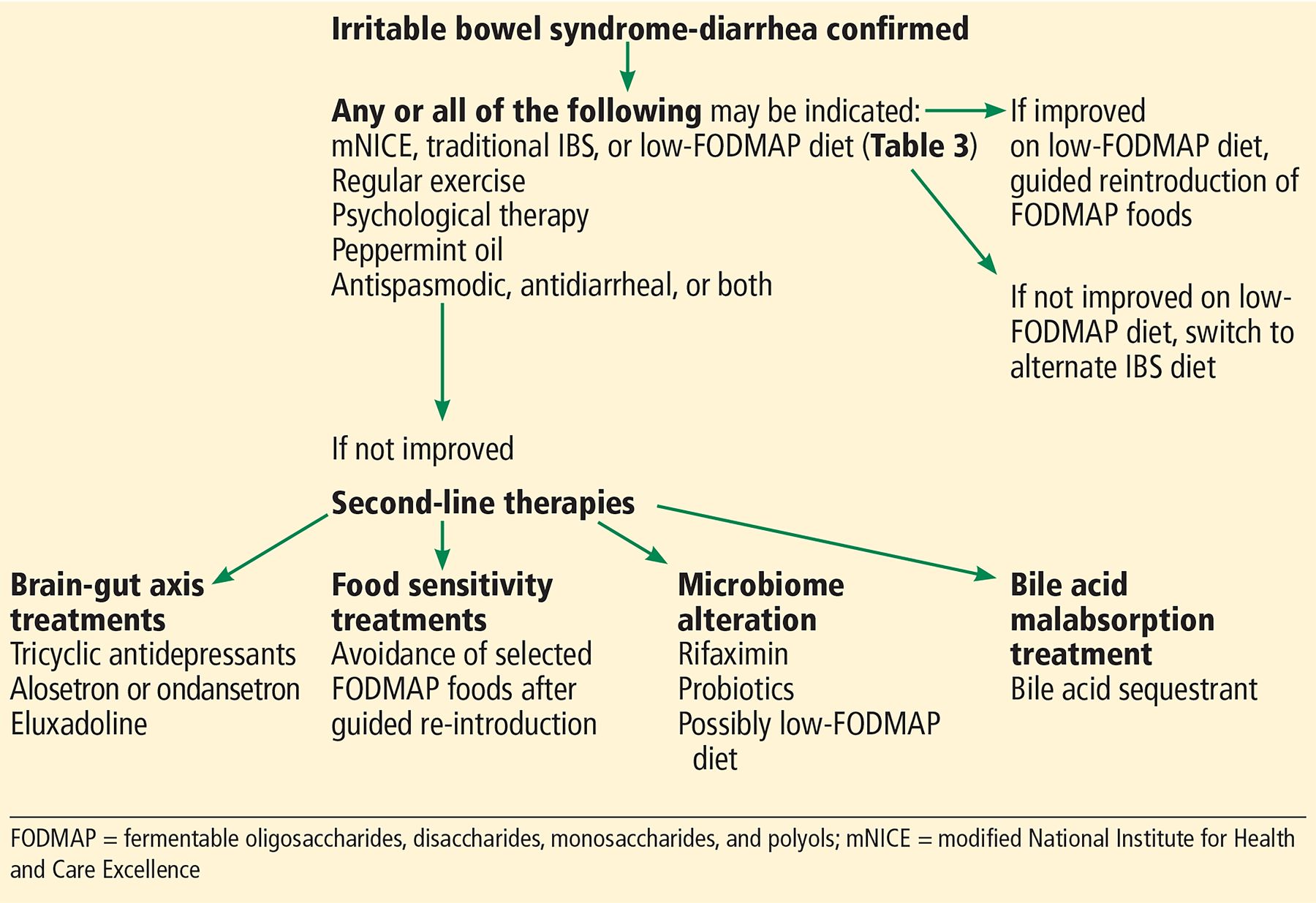
In addition, current drug treatment options, including discussion of new therapeutic targets are discussed. Functional constipation is not a result of a medical problem. This review summarises the diagnostic criteria to differentiate functional constipation from other causes of chronic constipation. Functional constipation Functional constipation is defined by criteria that include infrequent, hard, and/or large stools fecal incontinence painful defecation or volitional stool retention, if these symptoms are not explained by another medical condition, as outlined by the Rome IV consensus (table 1) 5,6. When these general lifestyle recommendations do not improve patients' symptoms, a step-wise and add-on treatment approach should be applied. In general, patients are initially advised to increase their fluid and fibre intake. Differentiation between these subtypes can be made through functional testing using tests such as anorectal manometry with balloon expulsion and a radio-opaque marker test. Functional constipation is characterized by decreased bowel movements and/or hard stools, which cause significant distress for children and their caregivers.

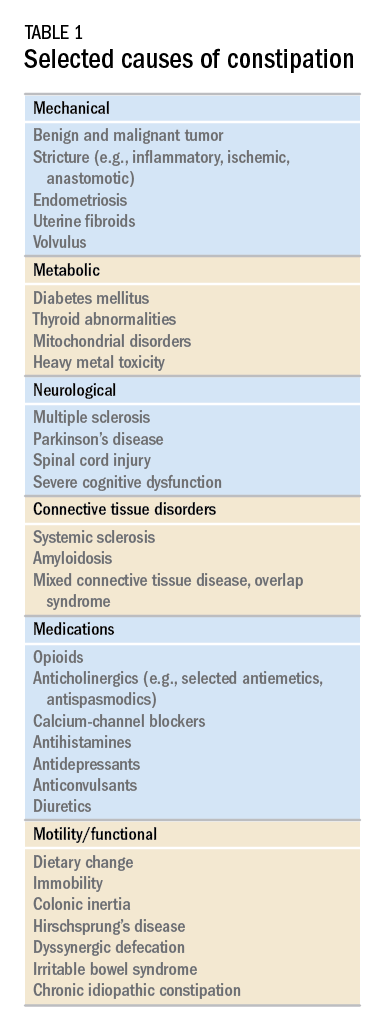
Three different subtypes have been identified to date: normal transit constipation, defaecatory disorders and slow transit constipation. Functional constipation is a common condition in childhood with significant impact on patients quality of life and on health care resources. In the absence of alarm symptoms, a confident symptom-based diagnosis can often be made using the Rome criteria. Chronic constipation is one of the five most common symptoms seen by gastroenterologist.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
